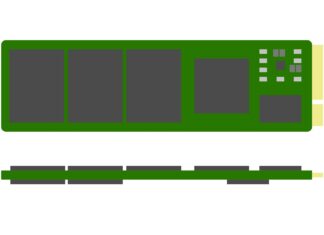
M.2 SSD Form Factor Explained
In recent years, the more compact M.2 form factor solid-state drives have taken over the traditional 2.5-inch in the market for high-performance storage. M.2, previously called Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF), is designed to...
Universal Flash Storage (UFS) Explained
What is UFS? UFS or Universal Flash Storage is a newer flash memory specification, with the intention to replace the slower eMMC (embedded MultiMedia Card) standard. It is designed by JEDEC, and was first...
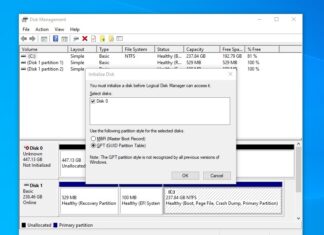
MBR vs GPT – Partition Table Explained
When you plug in a newly-purchased HDD or SDD to the computer, the operating system will often ask you to initialize the disk. Have you ever wondered what the differences between MBR and GPT?...
The 3-2-1 Backup Strategy Explained
Data backup is extremely important for everyone, especially when we keep almost everything digitally in this age. Whether it is a hard drive or solid-state drive, accidental damages and malfunctions are hard to prevent....
RAM Disks Explained
It is now common to see NVMe SSDs to reach speeds over 3 GB/s, or upwards of 6 GB/s for PCIe Gen 4 drives. With RAM disks, you can even get more storage performance...
Monitor Curvature Explained
Curved monitors have become more wide spread, whether they are a gaming-oriented displays or large 4K televisions. Based on your desk setup and preferences, you may want monitors to have slightly different curvatures. But...
PCIe vs SATA vs USB – Storage Interfaces Explained
As NAND flash technologies becoming more mature and advance in recent years, solid-state drives are now much more affordable and capable. Comparing with traditional HDDs, SSDs offers significantly better performance, especially on random read/write...
Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) Explained
802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) has been the mainstream Wi-Fi standard for quite some time now. Although 802.11ad was introduced with theoretical gigabit-capable throughput, it is limited in transmission range and lacks supported devices. Fortunately, new...